This tutorial is outdated. Soon I will update the blog post. For now you can refer to official Deno’s post.
In this post I would like to show how to build a GraphQL API server with gql.
At the moment there are a few GraphQL server modules for Deno, such as obsidian and oak_graphql but all of them are either standalone or framework-specific.
gql instead, is a framework-agnostic middleware so I will use it with Deno std’s http.
# GraphQL Schema
We’ll start with declaring a schema using type definitions and resolvers using graphql_tag and graphql_tools Deno modules, similar to how you do it with Apollo Server or GraphQL Yoga:
import { makeExecutableSchema } from 'https://deno.land/x/graphql_tools/mod.ts'
import { gql } from 'https://deno.land/x/graphql_tag/mod.ts'
/* Type definitions */
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`
/* Resolvers */
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: () => `Hello World!`,
},
}
const schema = makeExecutableSchema({ resolvers, typeDefs })
Now we have an executable schema that can be passed to a GraphQL server.
# Server setup
In order to setup gql you just need to pass a req object to it so it can read request body and properties.
import { serve } from 'https://deno.land/[email protected]/http/server.ts'
import { GraphQLHTTP } from 'https://deno.land/x/gql/mod.ts'
import { makeExecutableSchema } from 'https://deno.land/x/graphql_tools/mod.ts'
import { gql } from 'https://deno.land/x/graphql_tag/mod.ts'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: () => `Hello World!`
}
}
const schema = makeExecutableSchema({ resolvers, typeDefs })
const s = serve({ port: 3000 })
for await (const req of s) {
req.url.startsWith('/graphql')
? await GraphQLHTTP({
schema,
graphiql: true // enable GraphQL playground
})(req)
: req.respond({
status: 404
})
Now run the server with these permissions (for reading body and using network):
deno run --allow-net --allow-read server.ts
# GraphQL Playground
Now when then server is up, the GraphQL Playground will launch as well.
Open your favourite browser on http://localhost:3000 and you will see this:
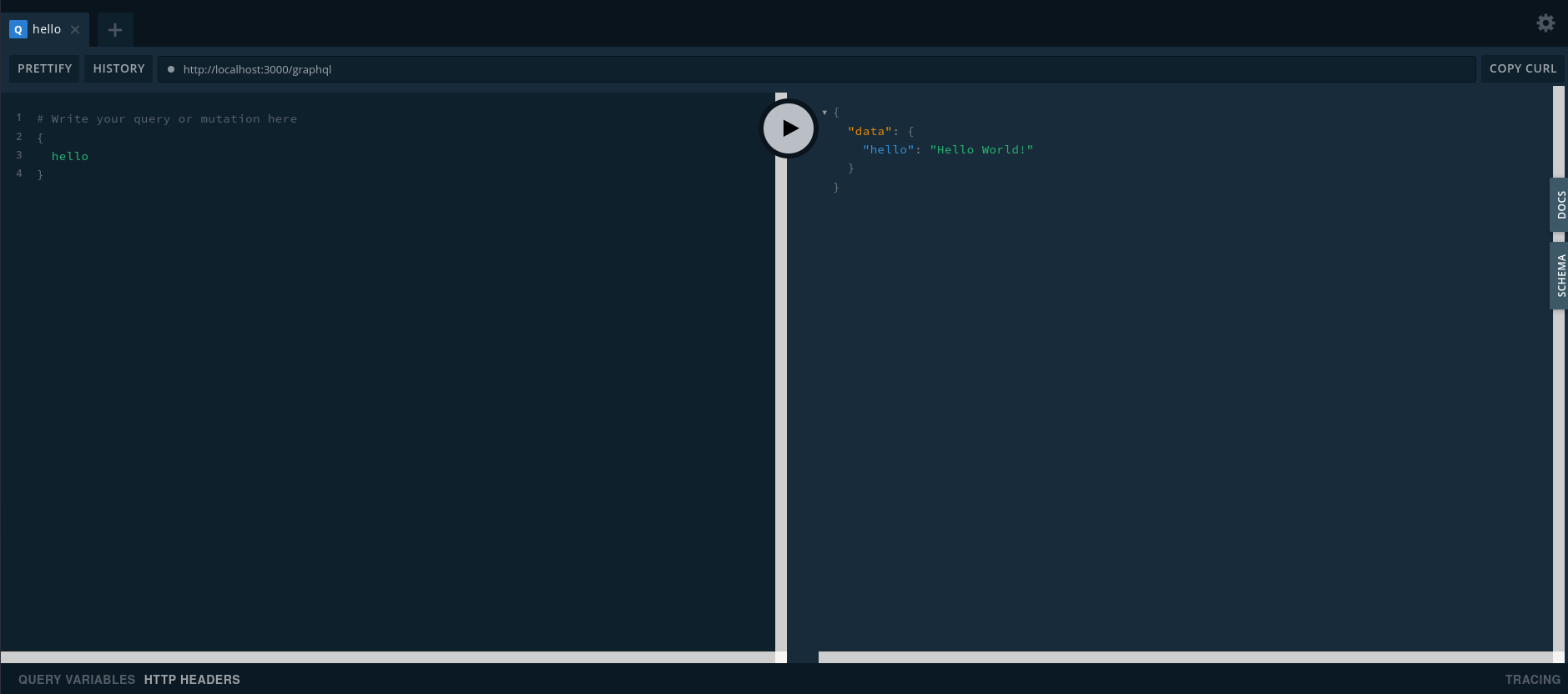
# Server Context
It’s also possible to pass request context to a schema so it could be used in resolvers. Request object is automatically passed to the context function.
import { serve, ServerRequest } from 'https://deno.land/[email protected]/http/server.ts'
import { GraphQLHTTP } from 'https://deno.land/x/gql/mod.ts'
import { makeExecutableSchema } from 'https://deno.land/x/graphql_tools/mod.ts'
import { gql } from 'https://deno.land/x/graphql_tag/mod.ts'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: (root, args, ctx) => `Hello World from ${ctx.url}! Cusotm context property ${ctx.ctxProp}`
}
}
const schema = makeExecutableSchema({ resolvers, typeDefs })
const s = serve({ port: 3000 })
for await (const req of s) {
req.url.startsWith('/graphql')
? await GraphQLHTTP<ServerRequest>({
schema,
graphiql: true // enable GraphQL playground,
context: (request) => ({
request, // request object
ctxProp: 'ctxValue' // aditional context properties
})
})(req)
: req.respond({
status: 404
})
# Conclusion
This is how you can set up a simple GraphQL server for Deno without any backend frameworks, just std/http.
Although, there are a few examples of using gql with other frameworks, check them out.
